
The pressure change can create a differential between the outer and middle ear that pushes the eardrum inward. Barotrauma of the ear also can happen when scuba divers descend. On an airplane, barotrauma to the ear – also called aero-otitis or barotitis – can happen as the plane descends for landing. Ear barotrauma can occur when these tubes become blocked or partially blocked. These bubbles are constantly moving into the middle ear, where they balance the ear's inner pressure. This is a bubble of air being moved through the Eustachian tube. When you swallow, you may notice a small click in your ears. This connects your ear with the back of your mouth.

The only connection between your middle ear and the "outside world" is a thin canal called the Eustachian tube. Your middle ear includes the eardrum and the space behind it. Generalized barotraumas, also called decompression sickness, affects the entire body. Last updated on Jan 12, 2022.īarotrauma refers to injuries caused by increased air or water pressure, such as during airplane flights or scuba diving. All the cranial nerves were.Medically reviewed by. Examinations of ear and nose were unremarkable. She had no addiction to tobacco and alcohol. She had a history of upper respiratory tract infection along with nasal congestion and cough for 3 weeks prior to flight. However, the facial weakness in the right side persisted, so attended our outpatient department. During descent of the flight, she felt little comfortable and leading to near complete resolution of the symptoms. The patient vitals such as blood pressure, pulse rate, and respiratory rate were within normal limits. The flight attendant helped with mid-air emergency service. During maximum elevation, she felt tingling sensation on the right side of the face and felt numbness over the face along with mild headache. She had increased sensation of pressure in his ears during ascent of the flight, but failed to relieve even after doing yawning or chewing gum or Valsalva.

He had a history of travel through flight where she developed facial weakness. We report a case of baroparesis in 38-year-old female who developed transient facial nerve paralysis while travelling on a commercial flight.Ī 38-year-old female attended the outpatient department of the Otorhinolaryngology with right side facial weakness since 3 days. The facial nerve palsy can be relieved by equalizing the pressure in the middle ear cavity through nasopharynx through eustachian tube. The development of the high pressure in the tympanic segment of the facial nerve may cause temporary ischemic neuropraxia which is thought to be the cause of the facial nerve palsy. This fallopian canal is a complicated bony pathway which is affected by the pressure changes. The facial nerve passes through the temporal bone via fallopian canal.
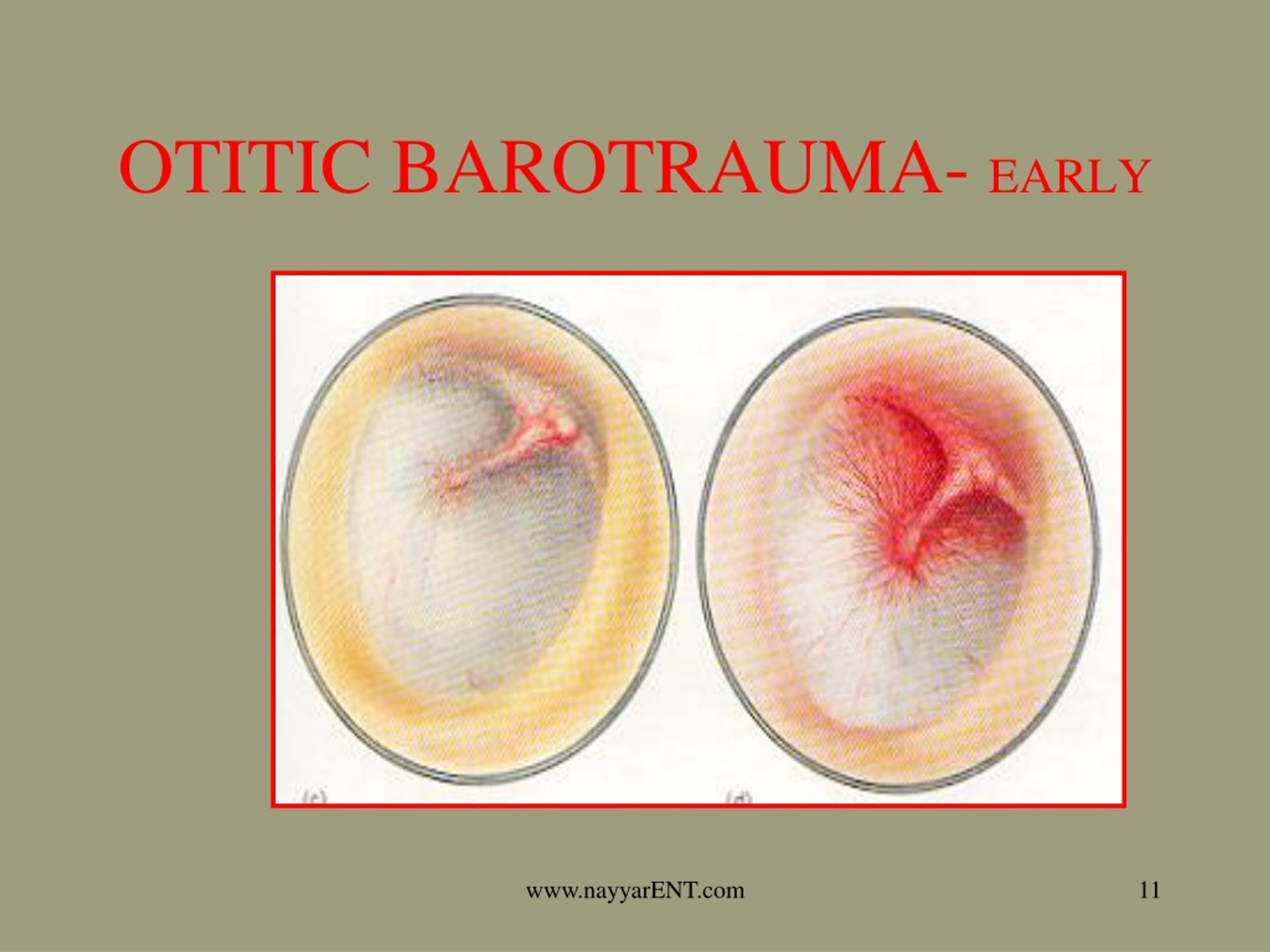
There are certain conditions which narrows the lumen of the eustachian tube such as edema, raised viscosity of the mucus coating of the tubal mucosal membrane or impairment of the tube to open. This may be due to impaired function of the eustachian tube. It is often reported in pilots or divers due to development of the high pressure in middle ear cavity. Here, we report a case of a 38-year-old female who experiences unilateral facial nerve paralysis on ascent to high altitude on a flight, with relieve from symptoms shortly after descent.įacial baroparesis is facial nerve palsy due to transient hypoxemia of the seventh cranial nerve secondary to raised pressure in the middle ear cavity. The clinical history and imaging help to diagnose this rare cause of facial nerve paralysis. The overpressure in the middle ear cavity due to eustachian dysfunction may cause exertion of the excessive pressure over the facial nerve through a dehiscence of the horizontal segment of the fallopian canal leading to facial nerve paralysis. It is rarely reported in medical literature which can happen among persons those ascend to high altitude in flight or scuba diving. Facial baroparesis is an extremely rare clinical entity which occurs due to otitic barotraumas.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
